Spider veins and varicose veins are two common vascular conditions that affect millions of people. While they may seem similar at first glance, these conditions have distinct differences in appearance, causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Understanding the key differences between spider veins and varicose veins can help you make informed decisions about your vein health and explore the best treatment options for your needs.
What Are Spider Veins?
Spider veins, also known as telangiectasias, are small, thin blood vessels that appear close to the surface of the skin. They are typically red, blue, or purple and form web-like patterns, often on the legs and face.
- Appearance: Thin, thread-like veins forming a spiderweb pattern.
- Location: Commonly found on the thighs, calves, and face.
- Symptoms:
- Typically asymptomatic.
- May cause mild itching or burning in some cases.
- Causes:
- Genetics, sun exposure, hormonal changes, prolonged sitting or standing, and certain medical conditions.
What Are Varicose Veins?
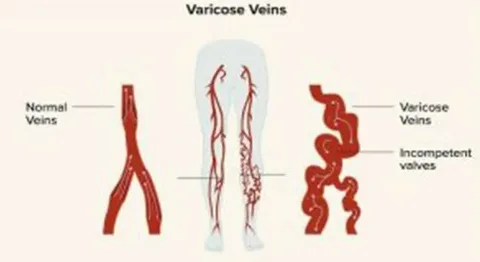
Varicose veins are enlarged, swollen, and twisted veins caused by weakened or damaged valves within the veins. They usually develop in the legs and feet, where blood flow is affected by gravity.
- Appearance: Bulging, rope-like veins that are blue or purple in color.
- Location: Primarily on the legs and feet.
- Symptoms:
- Aching, throbbing, or heaviness in the legs.
- Swelling around the ankles.
- Itching or skin discoloration near the affected veins.
- In severe cases, ulcers or open sores.
- Causes:
- Genetics, pregnancy, obesity, aging, and occupations requiring long periods of standing or sitting.
Both spider veins and varicose veins share similar risk factors, though the extent and severity may vary:
- Heredity: A family history of vein conditions increases the risk.
- Age: Aging weakens vein walls and valves.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and birth control use can contribute.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Reduces blood flow, leading to pooling in the veins.
- Obesity: Extra weight increases pressure on the veins.
- Sun Exposure: Especially for spider veins on the face.
Treatment OptionsSpider Veins:
- Sclerotherapy:
- A solution is injected into the veins, causing them to collapse and fade.
- Ideal for small and medium-sized veins.
- Laser Therapy:
- Uses focused light energy to target and eliminate veins.
- Effective for facial spider veins.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Regular exercise, elevating the legs, and wearing compression stockings can improve circulation.
Varicose Veins:
- Endovenous Ablation Therapy:
- Minimally invasive procedure using laser or radiofrequency energy to close off damaged veins.
- Vein Stripping and Ligation:
- Surgical removal of larger veins.
- Microphlebectomy:
- Removal of smaller varicose veins through tiny skin punctures.
- Compression Stockings:
- Provides support to reduce swelling and discomfort.
When to Seek Professional Help
While spider veins are often a cosmetic concern, varicose veins can lead to more serious health issues if left untreated. Consult a vascular specialist if you experience:
- Persistent pain or heaviness in the legs.
- Swelling or skin discoloration.
- Open sores or ulcers near the affected veins.
- Signs of blood clots, such as redness, warmth, or sudden swelling.
Although spider veins and varicose veins share some similarities, they differ significantly in appearance, symptoms, and severity. Understanding these differences can help you determine whether you need cosmetic treatments or medical intervention. If you’re concerned about the appearance or health of your veins, consult a vein specialist to explore the most effective solutions for your condition. Prioritize your vein health and regain your confidence today! Take care of your health, no matter what we are talking about – vein health, face care, chronic wounds.