Introduction: Security as the Backbone of Enterprise GenAI
As enterprises rapidly adopt generative AI to automate workflows, enhance decision-making, and personalize customer experiences, security and data privacy have become the biggest blockers to large-scale GenAI adoption.
Unlike traditional AI systems, generative AI interacts deeply with enterprise data, proprietary knowledge, customer information, and intellectual property. Without a robust GenAI security and data privacy architecture, organizations risk data leakage, regulatory violations, and loss of trust.
For enterprises, GenAI security is not an add-on—it must be architected from day one.
Why GenAI Security Is Fundamentally Different
Generative AI introduces unique security challenges because it:
- Processes unstructured and semi-structured data
- Uses prompts and context that may contain sensitive information
- Generates new content that can unintentionally expose data
- Often relies on third-party models or APIs
Traditional cybersecurity controls alone are not sufficient to protect GenAI systems.
Core Pillars of Enterprise GenAI Security Architecture
1. Data Isolation and Segmentation
At the foundation of secure GenAI architecture is strict data isolation.
Enterprises must ensure:
- Training data is isolated from inference data
- One business unit’s data cannot be accessed by another
- Customer data is logically and physically segmented
This prevents cross-contamination and unintended data exposure.
2. Secure Data Ingestion Pipelines
GenAI systems consume data from multiple sources such as:
- Internal databases
- Document repositories
- CRM and ERP systems
- Knowledge bases
Security best practices include:
- Encryption in transit and at rest
- Input validation and sanitization
- Data classification before ingestion
This ensures only approved and compliant data enters the GenAI pipeline.
3. Private and Controlled Model Access
Enterprises increasingly prefer:
- Private LLM deployments
- VPC-based model hosting
- Dedicated inference endpoints
This approach:
- Prevents enterprise data from being used to train public models
- Ensures full control over access, updates, and monitoring
- Reduces dependency risks on shared AI environments
Private access is essential for regulated and IP-sensitive industries.
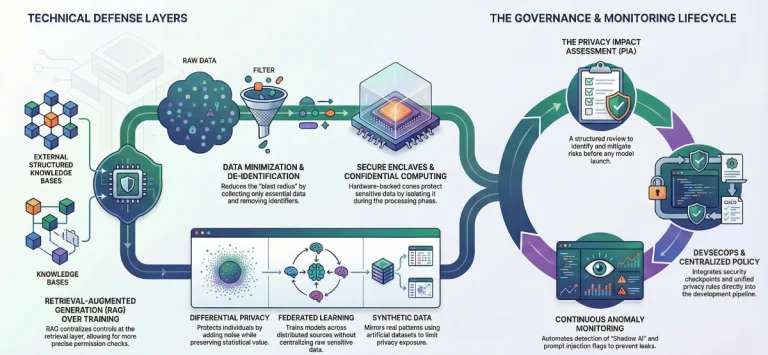
Prompt-Level Security and Privacy Controls
Prompts are a new and often overlooked attack surface.
Enterprises must implement:
- Prompt logging and monitoring
- Sensitive data masking in prompts
- Input filters to prevent prompt injection attacks
- Role-based prompt access controls
Prompt governance protects against data leakage and malicious manipulation.
Output Governance and Content Filtering
GenAI outputs can expose:
- Confidential data
- Biased or non-compliant content
- Inaccurate or misleading information
Security architecture must include:
- Output validation rules
- Policy-based content filters
- Human-in-the-loop approvals for critical outputs
This ensures AI-generated content aligns with enterprise policies and compliance standards.
Identity, Access, and Authentication Controls
Enterprise GenAI systems must integrate with existing IAM frameworks.
Key components include:
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Least-privilege access models
- API key and token management
Strong identity controls ensure only authorized users and systems interact with GenAI models.
Data Privacy by Design in GenAI Systems
Data privacy must be embedded across the AI lifecycle.
Privacy-first practices include:
- PII detection and anonymization
- Consent-aware data processing
- Data minimization principles
- Configurable data retention policies
This is critical for compliance with GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and other global regulations.
Monitoring, Logging, and Threat Detection
Continuous monitoring is essential for enterprise GenAI security.
Effective architectures include:
- Real-time usage monitoring
- Prompt and response audit logs
- Anomaly detection for unusual behavior
- Security alerts for misuse or breaches
This enables rapid incident response and forensic analysis.
Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
Enterprise GenAI security architectures must align with:
- Data protection regulations
- Industry-specific compliance standards
- Internal governance frameworks
Documented controls, audit trails, and explainable security mechanisms make compliance measurable and defensible.
Shared Responsibility Model in GenAI Security
Security responsibilities are shared across:
- Model providers
- Cloud infrastructure teams
- Enterprise IT and security teams
- Business owners
Clear ownership and accountability prevent security gaps and misconfigurations.
Role of GenAI Security Architecture Partners
Enterprises often rely on specialized partners to:
- Design secure GenAI architectures
- Implement private LLM environments
- Establish data privacy and governance frameworks
- Integrate AI security with enterprise SOC systems
- Enable secure scaling across business units
This accelerates adoption while minimizing risk.
Security as an Enabler, Not a Barrier
When implemented correctly, enterprise GenAI security:
- Builds trust among stakeholders
- Enables faster AI adoption
- Protects sensitive data and IP
- Supports regulatory readiness
- Unlocks enterprise-wide innovation
Security is not what slows GenAI—it’s what makes GenAI scalable.
FAQs
1. Why is GenAI security more complex than traditional AI security?
Because GenAI processes dynamic prompts, unstructured data, and generates new content, introducing new attack and leakage vectors.
2. Should enterprises avoid public GenAI models?
Not necessarily, but sensitive use cases require private deployments, strict data controls, and contractual safeguards.
3. How does GenAI security impact AI adoption speed?
Strong security frameworks actually accelerate adoption by reducing risk, increasing trust, and enabling broader deployment.